Introduction: Building the Supply Chain of Tomorrow

Today, the logistics industry operates in a world unlike ever before, facing pressure and challenges from rising customer expectations. Customers demand perfect, real time updates and complete transparency, which is increasingly difficult to deliver due to persistent labor shortages and the need to balanceoperational costs. In this environment, traditional manual processes are not just inefficient, but they slow down growth and competitiveness. For modern logistics companies, the choice is to move forward or risk being left behind.
The answer is logistics automation. This is not simply an improvement, but a complete rethinking of supply chain management. Companies can use automation solutions to achieve greater operational efficiency, productivity, and flexibility. This complete guide will focus on the real meaning behind a logistics automation system, the quantified benefits behind this automation technology, and a step-by-step plan. We shall focus on building blocks for every step of supply chain automation.
What is Logistics Automation? More Than Just Robots
Logistics automation is the process of dislocating specific logistically important activities with the help of minimal human intervention. The most common image is of autonomous vehicles or robots sliding through a distribution center, but that is certainly not the only one. There is a greater context: a true automation system is an intricate balance of hardware, highly sophisticated logistics automation software, and optimized processes that govern the entire supply chain. This chain stretches from the point an organization receives goods at a facility to the final-mile delivery to a consumer.
An ecosystem of this sort functions to arrange a seamless flow of information and materials. This balance comes from intelligent software, often integrated with an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, that directs the hardware. Consequently, a guideline is formed that guarantees every part moves together in concert. A key goal is to replace complex manual tasks, from order picking and packing to sorting and manual data entry, with tireless automated execution that improves order fulfillment.
The Core Business Benefits: Why Automation is a Strategic Investment

Implementing logistics automation is an investment that involves multiple facets, thorough guidance, and a considerable initial investment. Nonetheless, the value it drives is pivotal, ranging well beyond mere profit. It is critical for managers and decision makers to comprehend this multi-dimensional aspect of logistics automation, which is why industry leaders champion it as a forward-thinking investment, not a mere cost.
Driving Financial ROI and Cost Reduction
The most tangible result of introducing automation into logistics operations is on the bottom line. Automating repetitive tasks and reducing reliance on manual labor decreases overall labor costs and optimizes resource utilization. It is well known that warehouse automation increases the speed at which jobs are completed, boosting the overall throughput of a business. Automation is also a highly efficient process for reducing human error. In the business world, mistakes lead to costly returns and inventory discrepancies. Effective automation can also improve space utilization, decreasing overall expenses and maximizing the value of existing real estate.
Achieving Operational Excellence and Accuracy
Beyond cost savings, automation brings a new level of discipline and accuracy to warehouse operations. Automation systems remove the variation that comes with human performance. A robotic arm will perform heavy lifting and place an item with the exact same motion and accuracy, time after time, all day long. This accuracy alone drastically lowers picking errors, shipping mistakes, and errors in inventory control that plague many manual warehouses. A well-implemented warehouse management software provides complete visibility into every piece of inventory, enabling real-time inventory tracking. This level of control and accuracy creates a reliable and predictable operational environment, which serves as the core for any resilient supply chain.
Enhancing Speed, Safety, and Customer Satisfaction
In today’s market, performance standards are ever-evolving. The gap that remains unfulfilled in order fulfillment is often the time taken for order processing. Automation enables orders to be processed, packed, and dispatched quickly, leading to faster delivery times. Keeping the order velocity high boosts customer satisfaction and improves the overall customer experience. Customers are guaranteed to receive what they ordered, which minimizes errors and builds loyalty. Parallel to this, automation also improves workplace safety. Employees no longer have to perform physically demanding tasks within the set boundaries of what is usually considered safe.
Conclusion
To sum up, automation in logisticsis much more than a cost-cutting project, it is a long-term investment that drives competitiveness. Automation provides a real financial payoff by cutting costs, improving precision, and speeding up delivery, and it provides a base of operational efficiency. Meanwhile, it increases customer satisfaction by providing quicker and more dependable service and safer and more sustainable working conditions for employees. This multi-dimensional value makes automation a key force of resilience and expansion in a more dynamic market. To business leaders and decision-makers, the adoption of automation is not only a matter of fulfilling the needs of the present but also a foundation of future innovation and long-term success.
A 4-Step Roadmap to Implementing Logistics Automation
*The following video discusses 3 key trends driving Automation in Logistics, providing context for the 4-step roadmap.
Embarking on the automation journey can seem daunting. A structured, phased approach demystifies the process and ensures that the final solution is perfectly aligned with business objectives. Breaking the implementation down into four distinct stages provides clarity and control.
Phase 1: Analysis and Planning. This foundational stage is about understanding your current operations in granular detail. It involves mapping existing workflows and gathering key performance indicators (e.g., order cycle times, error rates, labor costs) through data analysis. The goal is to pinpoint the areas where automation will deliver the greatest impact. Based on this analysis, you can establish clear, measurable objectives for the project, such as “reduce pick-to-ship time by 30%” or “improveinventory management.”
Phase 2: Technology and Partner Selection. With clear goals in place, the focus shifts to finding the right automation tools and collaborators. This involves researching the various advanced technologiesavailable and evaluating which are best suited to your specific challenges. It is also the stage for vetting potential technology vendors and system integrators. A strong partner will not only provide the right hardware and software but will also offer deep expertise in system design and integration. Due diligence here is paramount to long-term success.
Phase 3: Deployment and Integration. This is the execution phase where the plan becomes a physical reality. It typically involves a phased rollout to minimize disruption to ongoing operations. The process includes site preparation, hardware installation, and software configuration. The most critical element is integration—ensuring that the new technologies communicate seamlessly with existing enterprise systems, such as your ERP. Rigorous testing is conducted to validate that all components are functioning correctly as a unified system.
Phase 4: Optimization and Scaling.The launch of the automated system is the beginning of a continuous improvement cycle. In this final stage, you will monitor system performance against the initial objectives, gather data, and make fine-tuning adjustments to optimize efficiency. This process can be enhanced with data analytics to derive valuable insights. As your business grows, this phase also involves planning for scalability, ensuring the automation solution can be expanded to meet future demand.
Key Technologies That Power Logistics Automation
Logistics automation is not a single technology but a combination of several. These systems integrate, with every system completing a unique task, to form a single efficient functioning system.
Core Software: WMS, TMS, and Management Systems
Automated operationsof the entire system are directed by software which provides streamlined intelligence. For the operational command center, Warehouse Management Systems(WMS) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS)perform administrator tasks. Nowadays, a WMS provides real time visibility and control over the entire warehouse, from managing inventory levels and directing retrieval systems to optimizing route planning and shipping. It provides both human and automated systems with detailed execution orders, allowing for effective resource allocation. For outbound logistics, a TMS provides similar functionalities, enabling route optimization and shipment consolidation to reduce overall delivery times and costs.
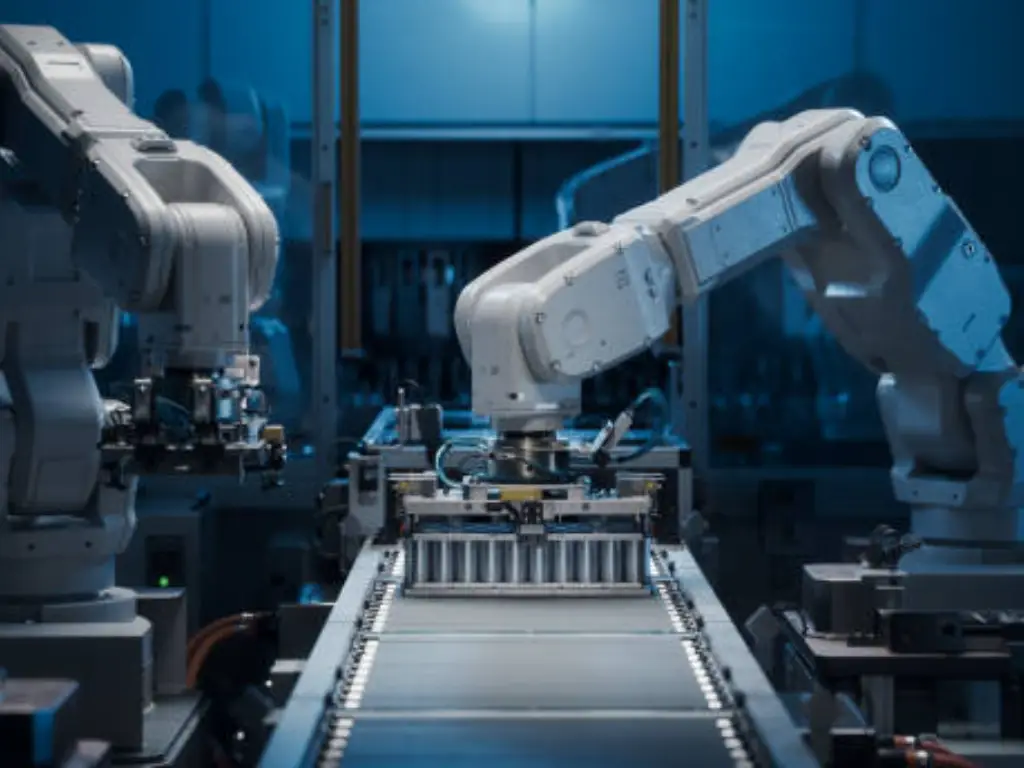
Physical Hardware: AGVs, AMRs, and Robotic Systems
This part includes all the hardware necessary for the actual moving and handling of goods. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)are a mature technology that follows set pathways to transport loads. More recently, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) have become popular due to their flexibility. They have sensors and use artificial intelligence to move through a facility and go around obstacles. They are usually used for “goods-to-person” picking, where an AMR moves inventory to an unmoving employee. Used with AMRs are robotic arms that have multiple purposes, including palletizing, depalletizing, and “piece picking.” Robotic process automationis a key part of this hardware ecosystem.
Material Flow: Conveyor and Sortation Systems
An example of goods flow through and between functional areas includes the receiving dock, picking, packing, and dispatching. To put these functional areas into practice, the use of conveyor belts and sortation systems is necessary. These systems allow for the movement of a large quantity of totes and cartons and are central to any sortation system. Modern sortation systemscan divide packages based on their destination to specific outbound lanes, churning out thousands of items each hour with a high rate of accuracy. These systems are vital in controlling the flow and order of a facility.
The Critical Role of Quality Parts in System Reliability
- Maximize Uptime: Reliable Quality, Delivered Fast
- Simplify Sourcing: 3,000+ Models from One Partner
- Built to Last: Lower Your Maintenance & Replacement Costs
- Tailored Solutions to Win Your Market
In the world of industrial automation, even the most advanced and complex systems ultimately rely on countless small and precise components to run reliably. The accuracy, stability, and longevity of the entire system often hinge on the quality of these essential parts. If a component fails at a critical moment, even the most sophisticated production line can come to a halt. That’s why we emphasize that achieving dependable system performance starts with uncompromising part quality—the very foundation of automation.
Take pneumatic products as an example: whether in gripping, lifting, or precise positioning, they play an irreplaceable role. Our cylinders, valves, tubing, and fittings deliver stability and smooth operation with the combined advantages of cost-effectiveness and high reliability. By reducing energy consumption and minimizing maintenance needs, these core components enable customers to optimize production costs while maintaining efficiency and consistency—securing the long-term smooth operation of the entire system.
As a dedicated manufacturer of industrial automation components, we believe that quality is the cornerstone of long-term trust. Our cylinder products are built to endure between three million and ten million cycles, far exceeding conventional requirements, effectively preventing downtime caused by part failures. Certified to international standards and backed by rigorous testing, our cylinders not only safeguard system reliability but also protect our customers’ long-term investments. Through continuous innovation and improvement, we ensure that every product helps eliminate risks at the source—strengthening both operational stability and competitive advantage.
Looking Ahead: Future Trends Shaping Logistics Automation
The logistics sector is always advancing, and it is certain that today’s technology is a precursor to more integrated systems. Numerous pivotal trends are shaping this future. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming more integrated, advancing beyond performing tasks to include predictive analytics. Future systems will more accurately forecast demand, predict equipment failures, and optimize logistics networks autonomously.
The Internet of Things (IoT)is another revolutionary force, creating a network of sensors that offer unparalleled perceptibility across the entire supply chain. This will facilitate real-time tracking of individual items and provide richer data streams to AI for data-driven decisions. Last, but not least, sustainability is a fundamental design principle. The industry is shifting toward more energy-efficient automation, route optimization to minimize fuel consumption, and waste avoidance in an operationally efficient manner. There are numerous case studies demonstrating these advancements.
Conclusion: Your Next Step Towards a Smarter Future

The path to staying competitive in the modern economy runs directly through logistics automation. It is the definitive strategy for overcoming persistent challenges of cost, efficiency, and customer demand. A successful implementation is a manageable process, and the benefits in terms of financial return,operational excellence, and customer service are profound.
The journey begins with selecting the right systems and technologies, but it is sustained by the quality of the components that form their foundation. The long-term success of your automation strategy ultimately hinges on the durability and precision of its foundational parts. Building a resilient and high-performing automated future requires an unwavering commitment to quality at every level, allowing your team to focus on more strategic activities.
Ready to build a reliable automation system from the ground up? Explore our range of high-performance automation parts or contact our experts to discuss the specific needs of your project.