In the modern automation industry where every millimeter of space is precious and every second of uptime is essential, designers and engineers are always seeking out effective and efficient components. We need accuracy and insist on dependability, and we have to operate within the physical limits of space and movement. It is in this challenging field that the rodless pneumatic cylinder, as a key member of the group of pneumatic cylinders, is introduced, not as an alternative, but as a major solution to some of the most nagging problems of automation.
This guide is for anyone who has had to contend with the awkward length of a conventional actuator or the danger of piston rod buckling during a long stroke. We are going to have a thorough examination of the world of rodless cylinders. This is not a product overview; it is your ultimate guide. We shall progress through the basic definitions to the complex mechanics of how it works, through the important process of selection and into its practical applications. When you have finished reading, you will have the knowledge and confidence to select the correct rodless cylinder to use in your next project, and turn a design limitation into a competitive advantage.
What Is a Rodless Pneumatic Cylinder?
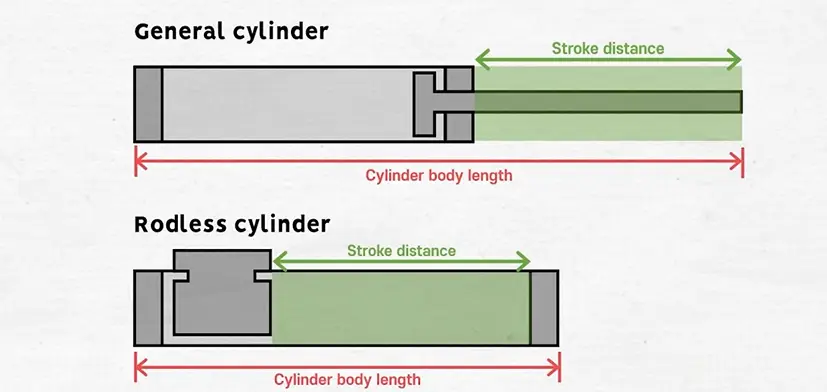
In essence, a rodless pneumatic cylinder is a linear drive that moves a load along the length of the cylinder without an external piston rod. This simple design modification leads to a smaller, space-saving solution over conventional pneumatic cylinders. The rodless type does not have this external rod, unlike the conventional version which uses a long, protruding steel rod to extend the force of the piston, and provides a clever and elegant solution to linear motion applications.
To see the benefit, take a common piston rod cylinder: it has a sealed tube, an internal piston, and a steel rod that extends when pressurized with compressed air. A 1-meter stroke needs not just a 1-meter-long cylinder but an additional meter of space to allow the extending rod to extend–so the effective working length occupies more than twice the actual stroke. This arrangement is efficient but inefficient in a space-constrained environment.
Rodless cylinders eliminate this by retaining the piston within the cylinder body and transmitting the force to an external carriage or shuttle which travels along the outer length of the cylinder. This enables the same stroke length to be used in a fraction of the space. The design also removes problems such as piston rod buckling in longer strokes, and rodless actuators are a perfect solution to engineers requiring long, stable linear motion in a small, self-contained package.
How Does a Rodless Pneumatic Cylinder Work?
*This video explains the internal structure and working principle of a rodless pneumatic cylinder.
The cleverness of the rodless cylinder is in the way it conveys the linear movement of the internal piston to the external carriage without a physical rod. This is achieved in two main coupling ways; magnetic and mechanical. The first step to the right tool is to understand the difference between these variants.
The Principle of Magnetic Coupling
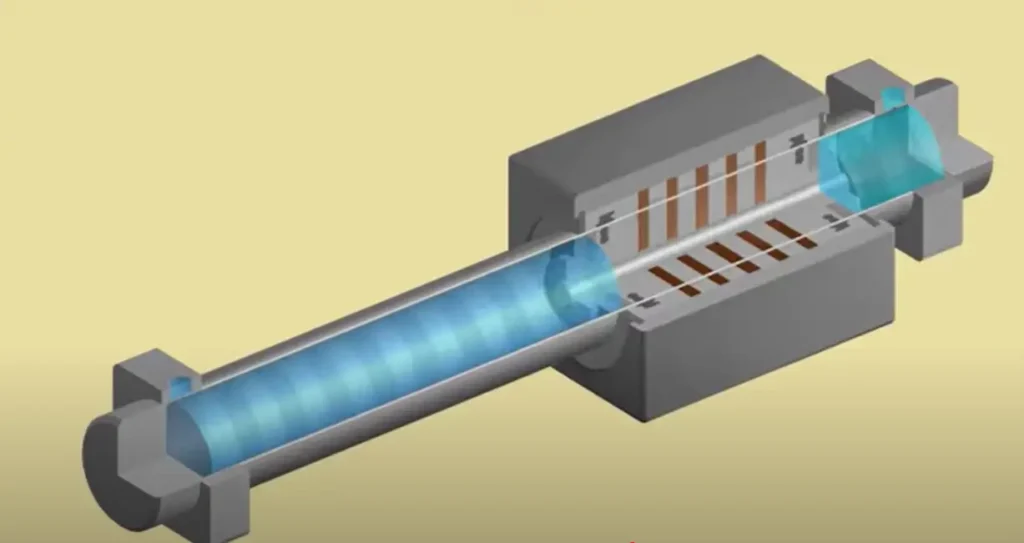


*The working principle of magnetically coupled rodless cylinder
The principle of non-contact force transmission is used in a magnetically coupled rodless cylinder. A ring of high-strength permanent magnets is mounted on an internal piston inside a sealed cylinder barrel. A mobile carriage outside the barrel has a matching set of magnets. These two sets of magnets are aligned perfectly to allow synchronized motion without direct mechanical contact.
When the compressed air is added, it pushes the internal piston through the length of the cylinder. The internal magnets create a powerful magnetic field as the piston moves, which penetrates the non-magnetic cylinder wall, usually aluminum or stainless steel, and is coupled with the external magnets on the carriage. This magnetic coupling enables the carriage to move in perfect synchronization with the piston, and the transfer of motion is smooth and reliable without any physical contact between the two parts.
The fully sealed and leak-proof structure is one of the main benefits of this design. The cylinder body has no mechanical openings, which means that the chances of air leakage or contamination are minimal. This is why magnetically coupled rodless cylinders are perfect in cleanrooms, food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing and other sensitive areas where hygiene and contamination control are paramount.
The Principle of Mechanical Coupling (Band Sealing)
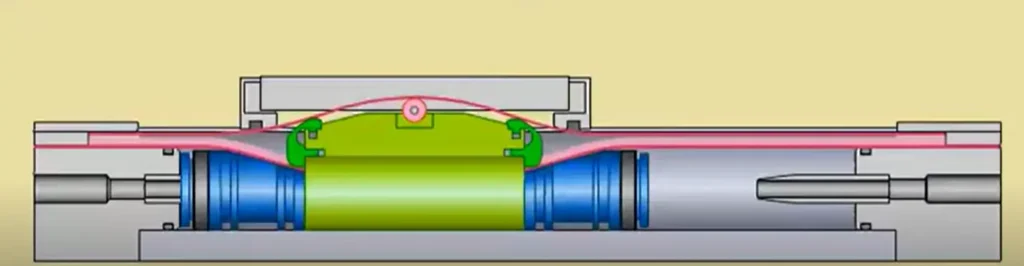
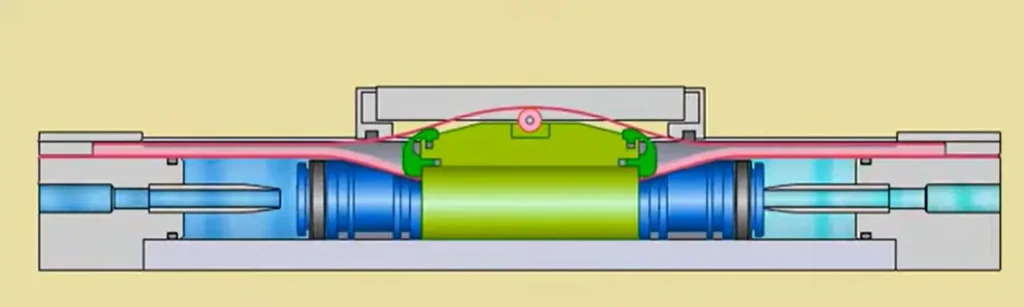

*The Principle of mechanically coupled rodless cylinders
Mechanically coupled rodless cylinders, in contrast, depend on a physical connection. These cylinders have a longitudinal slit which extends along the length of the aluminum extrusion, also known as the profile tube. A strong metal bracket extends through this slit and physically joins the internal piston to the external carriage.
A flexible, high-tensile sealing band, which is a band of steel on the inside and a band of a durable polymer on the outside, is placed to fit the slit perfectly to seal it. The piston, as it moves, raises the inner seal sufficiently to allow the connecting bracket to pass, and then, as it moves on, instantly forces the seal back into position. The outer sealing band guaranteesgood sealing properties.
This direct physical contact enables mechanically coupled rodless cylinders to support much greater loads, moments and acceleration forces than magnetic cylinders. They are the tough, high-performance actuators of the rodless world, and they dominate industrial applications that require power and precise control.
Key Advantages: Why Choose a Rodless Design?
The logical reason to use them is based on how they work. The innovative structure of rodless cylinders is converted into a package of strong benefits that can essentially enhance the design and performance of your machine. These are the major advantages of cylinders in this category.
- Space Savings: This is the main advantage. A rodless cylinder may save almost 50 percent of the required installation length over a rodded cylinder of the same stroke length. This is a great benefit in the time of small machine design.
- Suitable for Long Strokes: The longer the stroke length of a traditional cylinder, the more prone it is to sagging under gravity and bending under load. A rodless cylinder does not have such weakness. It is inherently stable and can be used to achieve longer travel strokes of several meters because its load is supported along the entire length of its body.
- Inherent Load Guidance: The external carriage of a rodless cylinder is usually made with a built-in guide bearing. This implies that it can support and guide the load directly, and is much better at handling off-center loads (moments) than a simple rodded cylinder, which usually needs a separate external guide system.
- High-Speed Capability:Rodless cylinders can frequently operate at higher speeds and more controlled acceleration and deceleration curves, resulting in faster cycle times and greater productivity, due to the absence of a long, oscillating piston rod to control. This is a key difference when compared to a standard electric actuator.
Rodless cylinders offer a flexible solution to the contemporary automation problems by combining the load-carrying and motion capabilities in a small, efficient package. Their special features create new opportunities in system design where conventional alternatives are inadequate.
Critical Selection Criteria: How to Size Your Cylinder Correctly
Selecting a rodless cylinder is a more subtle process than selecting other standard pneumatic drives. To be successful, one has to consider a number of important parameters. This is what makes the difference between a machine that works perfectly and one that wears out prematurely and fails.
- Load & Force Calculation: This is the beginning. You should calculate the mass of the load (in kg) you are transporting and the force needed to accelerate it to the required speed. Never forget friction and a safety margin, especially for applications with a high load.
- Stroke Length & Speed Requirements: The required travel distances (stroke) are simple. The speed will, however, affect the calculations of force and might require cushions or shock absorbers at the end of the stroke length to control the deceleration.
- Orientation & Moment Loads: This is probably the most important and most neglected step. A load is seldom exactly in the middle of the carriage. This produces moment loads-torques that attempt to twist the carriage. It has three types of axis movement:
- Pitch (My): A rotational force that goes up and down.
- Yaw (Mz): A rotational force that rotates side to side.
- Roll (Mx): A rotational torque about the travel axis. Each manufacturer will have a catalog, often with CAD models, that will give maximum allowable moment values of each cylinder. The quickest way to destroy the guide system is to exceed them. You should also compute the moments that your application will produce and make sure that they are within the specifications of the cylinder.
- Environmental Factors: In which environment will the cylinder be used? A food grade application requires stainless steel construction and a magnetically coupled design. A foundry or woodshop might need improved seals and scrapers to guard against abrasive dust. Seals and lubrication may be influenced by high or low temperatures. The materials and construction of the cylinder should always be matched to the working environment. Consider installing sensors to monitor performance in harsh conditions.
Considering all these parameters, including the calculation of the force requirements, the assessment of the environmental factors, will guarantee that your rodless cylinder will work reliably and efficiently. Ignoring any of them may undermine the durability and accuracy of the system. By selecting the capabilities of the cylinder to precisely meet the requirements of your application, you will establish the basis of a durable, easy to maintain solution that will perform reliably over the long term.
Common Applications Where Rodless Cylinders Excel
The theoretical benefits of rodless cylinders are realized in their enormous wide variety of pneumatic applications. They are invisible engines that power productivity in numerous sectors.
| Application Area | Typical Uses | Key Advantages |
| Material Handling | Ideal for long transfer systems, cross-conveyor pushers, and diverter gates where smooth, long motion is required. Custom systems often rely on them. | Suitable for long-distance, smooth motion handling. |
| Automated Assembly | Used to place parts into robotic arms or move components between workstations. Their compact size and accuracy are perfect for complex assembly lines. | Compact and precise—ideal for tight assembly setups. |
| Packaging & Palletizing | Commonly used in case packing, box opening, and transferring products to pallets. The long stroke capability is a major benefit. | Long stroke enhances efficiency in packaging tasks. |
| Special Machinery | Drives screen printing squeegees, opens/closes large safety doors, positions spray nozzles, and powers textile machinery—anywhere controlled linear motion is needed in tight spaces. Valves enable precise control. | Precise control and space-saving for specialized tasks. |
Whether it is material handling or special machinery, rodless cylinders are worth their weight in gold because they provide dependable linear motion in tight areas. Their flexibility, accuracy and long stroke capabilities make them a key part of modern automation, and they continue to be the performance driver where space and efficiency are paramount.
Why Your Choice of Manufacturer Is as Critical as the Cylinder Itself
Now you know what, how and why of rodless cylinders. You are able to compute forces and determine moment loads. However, there is one last, very important piece of the puzzle: the relationship you establish with your component manufacturer. You may design the ideal cylinder on paper, but its actual performance, its reliability, its life, its final value, is inseparably bound up with the quality and skill of the people who made it.
The journey starts with the knowledge of the technical parameters. It is one thing to have that knowledge and quite another to turn it into a long-lasting, efficient machine, and that is where a real manufacturing partner earns their stripes. They are able to convert the theoretical benefit of a rodless cylinder into real ROI for your business.
Beyond the Spec Sheet: Our Commitment to Your Application’s Success

At Hebai-omch, we don’t just manufacture rodless pneumatic cylinders—we engineer solutions that drive success in real-world applications. With over 37 years of experience, we’ve learned that meeting a technical specification is only the beginning. Our cylinders are trusted across automation, packaging, food and beverage, and automotive industries not just for their stroke length or bore diameter, but for how they perform under real-world pressures, temperature changes, and operating cycles. We make sure every product we deliver can integrate seamlessly into your workflow and perform with consistency—even in the most space-constrained or high-demand environments.
Our long-stroke rodless cylinders—customizable from 10 mm up to 2000 mm in stroke and Ø12 mm to Ø320 mm in bore—are built for versatility. But we go further. We tailor material selection, mounting options, and performance specs to your environment, whether you’re automating a cleanroom facility or building a rugged distribution system. Every solution is backed by IP65–IP68 ratings, overload protection of up to 200%, and a service life that reaches up to 10 million cycles. These aren’t just numbers—they reflect our promise of reliable operation, reduced downtime, and long-term ROI for your investment.
What truly sets Hebai-omch apart is our comprehensive support—from OEM customization and CNC secondary processing to same-day shipping from our stocked warehouses. We provide one-stop purchasing with 24/7 support, ensuring you can move from concept to production without delay. Whether you need CE- and RoHS-certified components or custom-engineered cylinders for a new product line, our commitment is clear: delivering beyond the spec sheet, with reliable performance, fast delivery, and expert support every step of the way.
Conclusion: The Smart, Space-Saving Choice for Modern Automation
The rodless pneumatic cylinder is more than just a component; it’s a design strategy. It represents a commitment to efficiency, smart use of space, and robust performance over longer travel distances. From its clever mechanics to its wide-ranging applications, it stands as a testament to engineering that solves real-world problems.
We’ve journeyed through its core principles, its key advantages, and the critical path to selecting the right one. But remember, the final step in ensuring success is choosing a partner who values your application as much as you do. A successful outcome is born from the fusion of a correctly specified product and a reliable, expert manufacturer. Make the smart, space-saving choice, and watch your automation reach new heights of performance. Our team is ready to help you get there. Choose Hebai-omch for rodless cylinders that combine certified quality with rapid delivery—trusted by thousands since 1986. Let our decades of expertise turn your automation challenges into streamlined, space-saving solutions.